How Scammers are Using AI To Target Web3 Users

With recent advancements in generative AI (like LLMs, deep fakes, and voice cloners), we’re seeing many new opportunities for innovation in the Web3 space. But alongside those looking to leverage this technology for good, there are malicious actors who are leveraging generative AI to develop new methods for scams that take advantage of Web3 communities.
Leading AI companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google are actively shipping updated models that are increasingly intelligent, cheaper, and easier to access and use. Often, companies building AI models will share some details around their models with the intention to support users. But unfortunately, malicious actors can leverage that same information to reverse engineer new and more advanced scams.
3 Ways That Scammers Leverage AI to Target Web3 Users
With the goal of taking advantage of a brand or their community, scammers will typically choose a strategic method for targeting an organization, or their community. Let’s unpack three of the most widely used ways that malicious actors are leveraging AI to scam Web3 users.
1. Domain Impersonation
Impersonation is one of the most common ways that scammers leverage AI to target Web3 users. The scammers will use AI to generate a list of the most obviously similar websites to an organization’s legitimate website, and then re-structure and rebuild the copied website in seconds.
This strategy is already used on a large scale. For security companies using automation, this usually means that a 1:1 similarity match can’t be done. This is because the website is slightly modified to be visually and structurally different from the organization’s original, legitimate website.
2. Deep Fakes and Cloning
Deep fakes and voice cloning leverage generative AI to create impersonations of real people. A deep fake is a video or image of a person in which their face or body has been digitally manipulated so that they appear to be someone else.
Voice cloning involves using speech from the target voice to train an AI model. The model learns the voice’s vocal patterns, intonations, and nuances, enabling it to generate speech that sounds like the original speaker.
In Web3, scammers may use deep fakes or voice cloning to impersonate well-known figures or to spread misinformation. For example, bad actors may create a deep fake of Elon Musk to trick users into believing that they need to claim an upcoming token distribution.
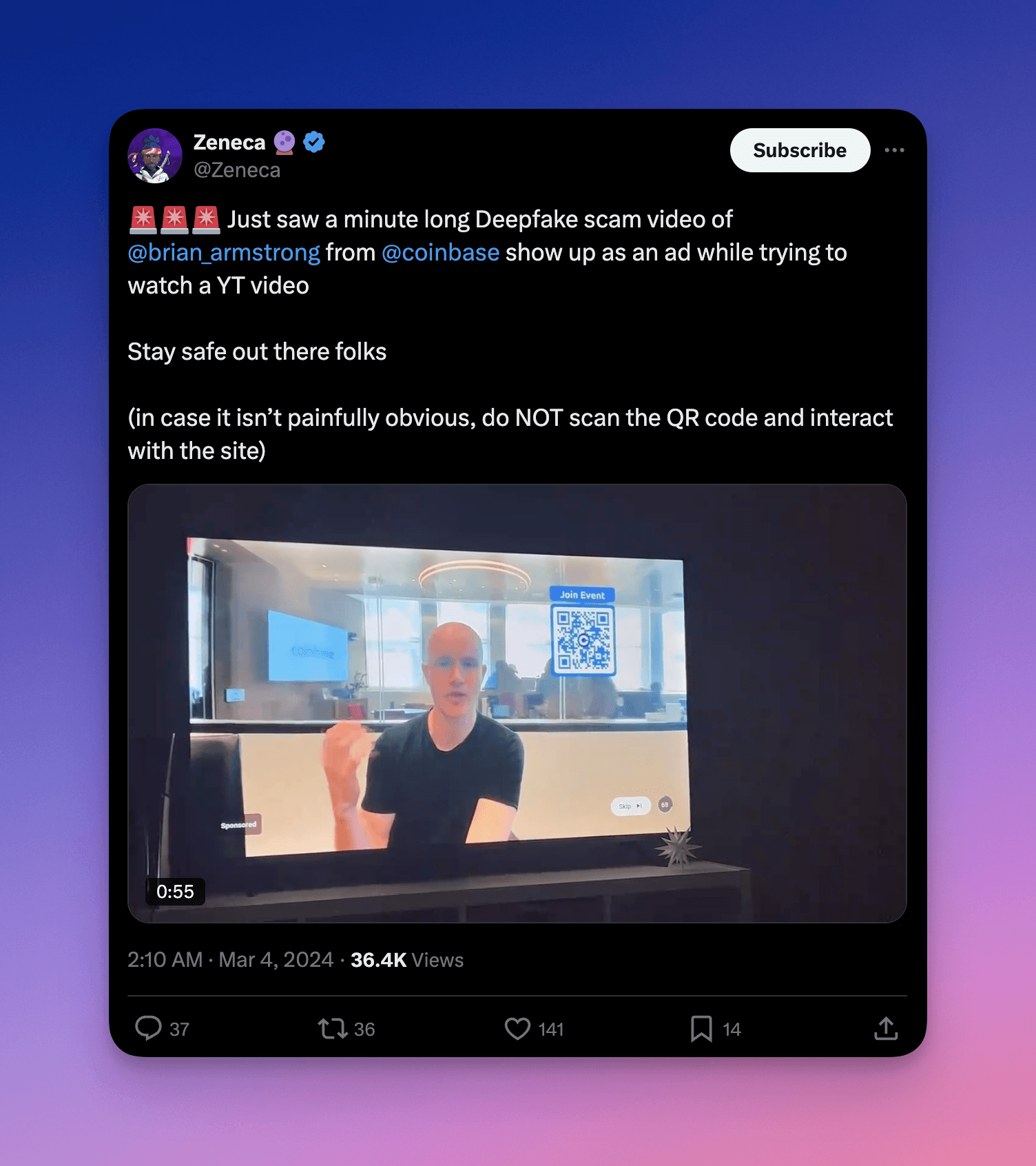
Deepfake of Brian Armstrong, CEO of Coinbase
3. Phishing
AI helps scammers send a high volume of fake emails and texts that look real. These messages might say they’re from a crypto exchange, asking you to click a phishing link or to give them your account info, or they offer you an opportunity to make a passive income off the AI-powered trading bot.
Sometimes, you might even engage with a “real person” on X or other social media. Behind the scenes there is a specific program written to engage with you, with the final goal of sharing a phishing link or bringing your attention to a certain area.
Other evolving methods exist, but phishing and impersonation are still the most common ways to steal funds. It’s incredibly important to be informed of these common scams because if you interact with a malicious website, your crypto wallet funds are gone. Always know and practice Web3 security tips to keep your funds secure.
The Impact of AI-Based Threats in Web3
AI advancements have made it possible for malicious actors to operate smarter and on a large scale. That doesn’t mean every threat drains significant capital, but it does mean that threats are often indistinguishable from legitimate websites.
If 1-5% of all the websites spread by malicious automation resources are going to hit the users with at least $100 in their crypto wallet, then the scammers’ computational costs are covered and possibly expanded to more significant capital if they get lucky.
How ChainPatrol Protects Web3 Brands From AI Threats
At ChainPatrol, we know that a company that does not adopt AI will be left with stale analysis systems that are irrelevant to the scam techniques that are evolving with AI. Given this, we constantly seek ways to counter AI-based attacks on communities, companies, and their members.
Apart from traditional methods of identifying malicious intent, such as algorithmic image similarity, keywords, content analysis, checking legitimate sources, looking through customer social media, and more, we also actively adapt our system to use the latest AI advancements that contribute to existing detection.
Here are three strategies we are already leveraging to counter AI-based threats in the Web3 ecosystem.
1. Content Similarity Analysis
Malicious websites appear similar to legitimate assets, but have differentiators that make them challenging to detect. Due to that, using LLMs to analyze key website information, meta tags, and DOM structure has become a must for any threat detection system.
By leveraging these tactics, ChainPatrol is able to gather a solid explanation of the overall score collected from LLM, which can contribute to the final touch on auto-blocking malicious assets.
2. Detecting Impersonation Attempts
Sometimes, understanding if a certain asset is indeed an impersonation of a brand can be challenging, even for internal members of the organization that’s being impersonated. This is because the differentiators can be very subtle, making it almost impossible for traditional detection systems to detect an impersonation attempt. With LLMs, it becomes incredibly more straightforward to detect malicious content.
3. Threats Classification
We analyze social media, search engines, and the internet overall for different types of assets, as well as collect threats that other people send to us via API or UI. It’s essential to understand that human error can occasionally happen when certain threats are grouped to specific organizations so that the threat volume can be precisely understood and reviewed can be run for an appropriate organization. As you can imagine, AI-based features within the system helps us triage and process threats coming into our system.
These are just a few of the many strategies that ChainPatrol is leveraging to counter AI-based Web3 threats on a large scale.
The Future of AI and Online Threats
The rise of generative AI presents new opportunities for both innovation and exploitation in the Web3 space. Scammers are increasingly using AI for impersonation tactics, like deep fakes and phishing schemes, to deceive users.
These AI-powered scams make it harder to distinguish legitimate websites and communications from fraudulent ones, which can pose significant risks to Web3 security.
At ChainPatrol, we recognize these evolving threats and are using advanced AI-based detection strategies to combat them, such as content similarity analysis, impersonation detection, and threat classification. We help protect Web3 communities from increasingly sophisticated attacks by staying ahead of AI-enabled scams.
Are you ready to protect your brand and community? Book a ChainPatrol demo to learn how we can help.